CFS
Food Safety Focus (150th Issue, January 2019) – Food Safety Platform
Histamine in Fish and Fish Products
Reported by Mr. Kenneth Yung, Research Officer,
Risk Assessment Section, Centre for Food Safety
Fish is an important part of many types of cuisine that we savour. However, the consumption of fish and fish products containing high level of histamine may cause scombrotoxin fish poisoning (SFP), also called histamine poisoning. In Hong Kong, the Centre for Health Protection of the Department of Health recorded a total of 26 local SFP cases, affecting 45 persons from 2009 to 2018. In this article, we discuss how histamine is formed and the ways to control level of histamine in fish and fish products..
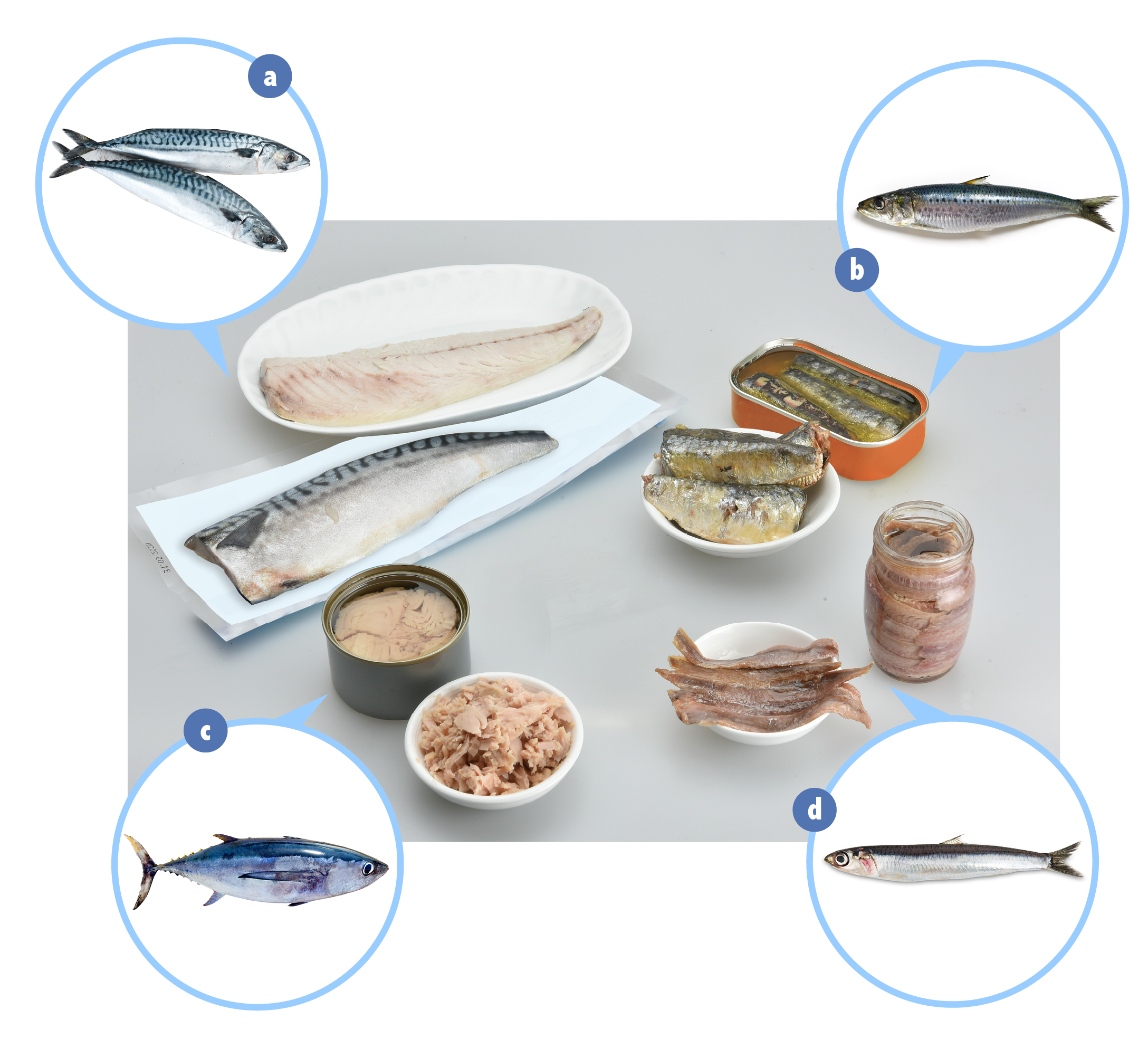

Examples of fish which contain elevated levels of naturally occurring histidine: (a) mackerel, (b) sardine, (c) tuna and (d) anchovy. Some of their respective products have also been found to contain high levels of histamine.
Formation of Histamine in Fish and Fish Products
Histamine is a toxic metabolite produced by histamine-producing bacteria during spoilage and fermentation of fish and fish products. Many histamine-producing bacteria are part of the natural microflora of the skin, gills and gut of freshly caught fish. Histidine decarboxylase (HDC) enzymes, synthesized by histamine-producing bacteria when they multiply, convert the amino acid histidine that are naturally present in fish into histamine.
The level of histamine in fish and fish products mainly depends on species of fish and time-temperature control. Certain fishes like mackerel, sardine, tuna and anchovy naturally contain high amount of histidine and have been associated with SFP cases in Hong Kong and/or other places.
Time and temperature control is the most effective method for ensuring food safety for fish species prone to histamine production. In the absence of proper time-temperature control such as refrigeration and freezing, formation of histamine may occur at any point throughout the supply chain. Previous study conducted jointly by the Food and Environmental Hygiene Department and the Consumer Council revealed that high levels of histamine (up to 2600 mg/kg) that can cause SFP were detected in opened canned fish samples that were left at room temperature for 24 hours. However, histamine was not detected in samples that were kept at 2°C for up to 168 hours.
Health Effects of Histamine
SFP is caused by the ingestion of food containing high levels of histamine i.e. consuming a serving size of 250g fish or fish product with histamine level exceeding 200 mg/kg may cause symptoms in healthy individuals. Symptoms of SFP include tingling and burning sensation around the mouth, facial flushing and sweating, nausea, vomiting, headache, palpitations, dizziness and rash. Exacerbation of asthma and more serious cardiac manifestations were reported in more severe cases. The onset of symptoms is within a few hours after consumption and these symptoms will normally disappear in 12 hours without long term effect.
Control of Histamine in Fish and Fish Products
High levels of histamine can build up in fish and fish products before any signs of spoilage (e.g. bad smell or taste) develop. Therefore, measures for control of histamine should be taken along the food chain from harvest to consumption.
Care should be taken that the cold chain is maintained at or below 4°C along the supply chain, including points of transfer such as offloading of fish from the vessel and processing procedures. Frozen fish and fish products should be kept at or below -18°C. Transport vehicles or vessels should be adequately equipped to keep fish cold and pre-chilled before loading fish where applicable. Adequate heat treatment (e.g. cooking, hot smoking) can kill histamine-producing bacteria and inactivate HDC enzymes, but cannot destroy pre-formed histamine. Recommendations in the Code of Practice for Fish and Fishery Products (CAC/RCP 52-2003), issued by Codex Alimentarius Commission, should be observed to ensure food safety.
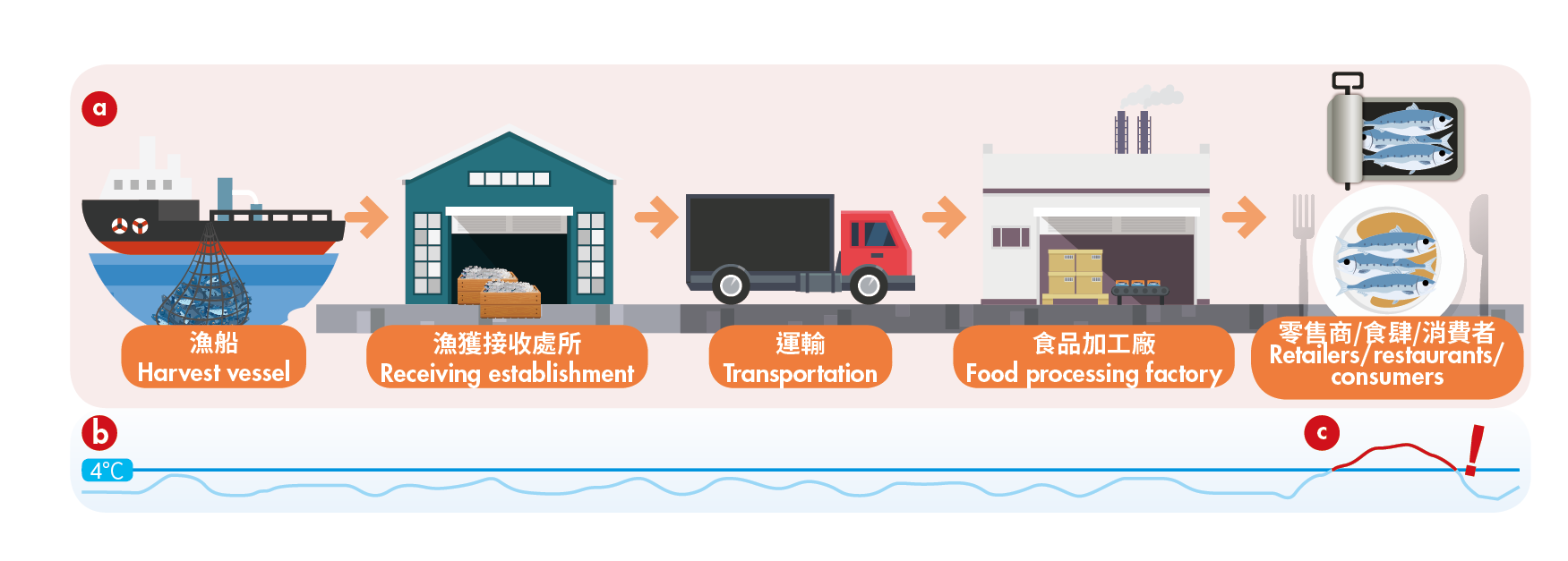
(a) Cold chain should be maintained throughout the whole supply chain. (b) Refrigerated fish and fish products should be kept at or below 4°C. (c) The time which fish products are kept under ambient temperature should be minimised.
At the consumer level, fish should be chilled rapidly after purchase. For pre-packaged fish and fish products, store according to the instructions of the manufacturer (e.g. keep refrigerated). If cooked fish and ready-to-eat fish products (e.g. tuna fish sandwiches and opened canned fish) are placed at room temperature all day long, they can be re-contaminated and histamine can form. Therefore, if these foods are not being eaten immediately, they should be kept under refrigeration and be finished as soon as possible.






