MPI
New Zealand Food Safety is extending its advisory to the public not to collect or consume shellfish gathered from the East Coast of the North Island due to the presence of paralytic shellfish toxins.
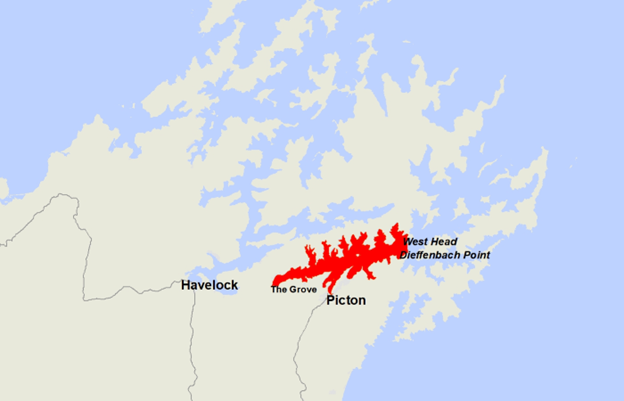
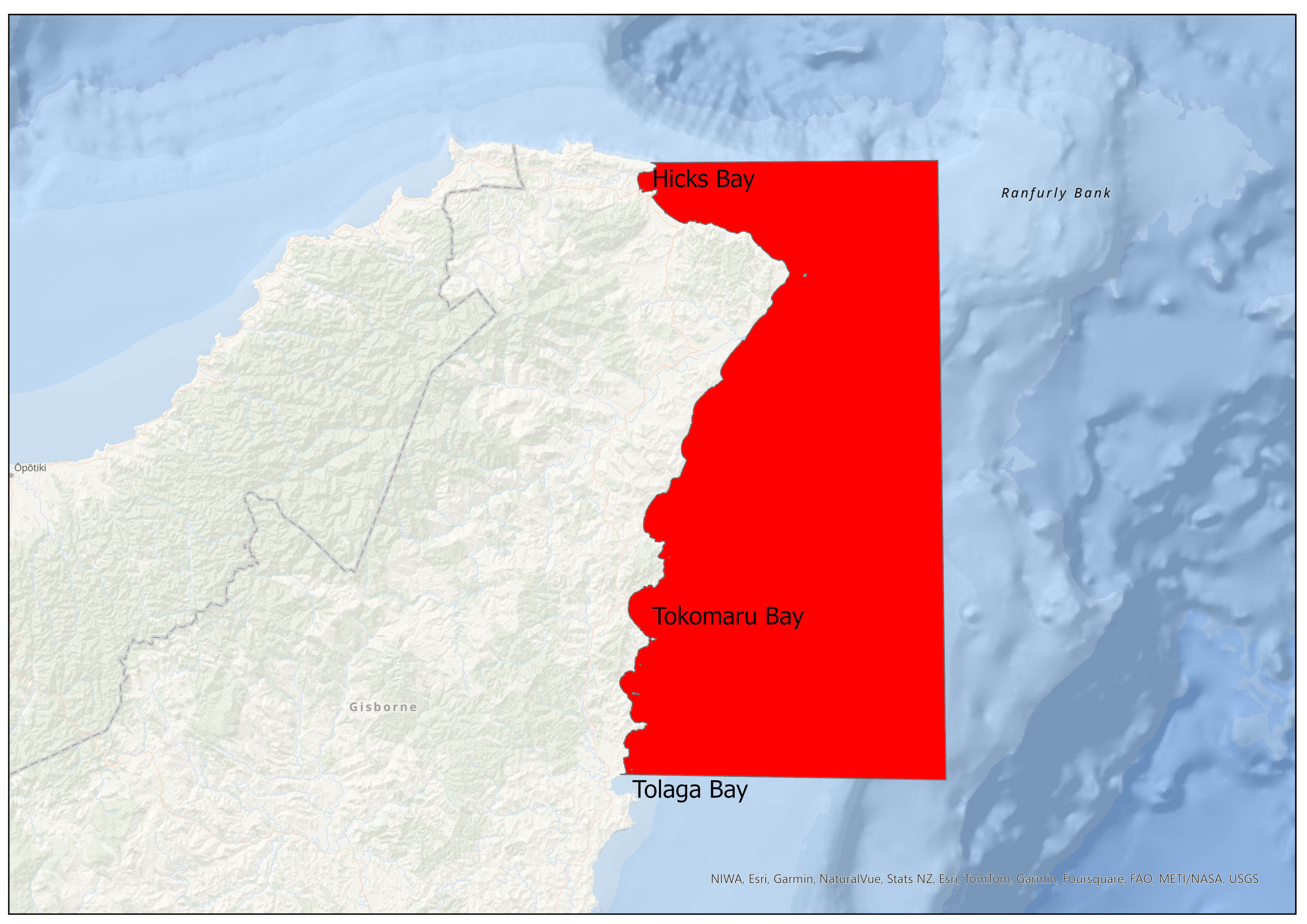
“We have extended the existing warning north to now span from Cape Runaway all the way south to Blackhead Point, which is just north of Pōrangahau. Follow-up tests on mussels from Hicks Bay Beach showed levels of paralytic shellfish toxins three times the safe limit,” says New Zealand Food Safety deputy director-general Vincent Arbuckle.
“Please do not gather and eat shellfish from this area because anyone doing so could get sick. Affected shellfish include bivalve shellfish such as mussels, oysters, tuatua, pipi, toheroa, cockles, and scallops, as well as pūpū (cat’s eyes), Cook’s turban and kina (sea urchin).
“We are monitoring an algal bloom off the East Coast, which is spreading. This type of algae produces a dangerous toxin and when shellfish filter-feed, these toxins can accumulate in their gut and flesh. Generally, the more algae there are in the water, the more toxic the shellfish get.
“Cooking the shellfish does not remove the toxin, so shellfish from this area should not be eaten.”
See a map of the warning for East Cape
Symptoms of paralytic shellfish poisoning usually appear within 10 minutes to 3 hours of eating and may include:
- numbness and a tingling (prickly feeling) around the mouth, face, hands, and feet
- difficulty swallowing or breathing
- dizziness and headache
- nausea and vomiting
- diarrhoea
- paralysis and respiratory failure and, in severe cases, death.
Pāua, crab, and crayfish may still be eaten if the gut has been completely removed prior to cooking, as toxins accumulate in the gut. If the gut is not removed, its contents could contaminate the meat during the cooking process.
Finfish are not affected by this public health warning, but we advise gutting the fish and discarding the liver before cooking.
New Zealand Food Safety has had no notifications of associated illness.
If anyone becomes ill after eating shellfish from an area where a public health warning has been issued, phone Healthline for advice on 0800 61 11 16, or seek medical attention immediately. You are also advised to contact your nearest public health unit and keep any leftover shellfish in case it can be tested.
“We are monitoring shellfish in the region and will notify the public of any changes to the situation,” says Mr Arbuckle.
Commercially harvested shellfish – sold in shops and supermarkets or exported – is subject to strict water and flesh monitoring programmes by New Zealand Food Safety to ensure they are safe to eat.