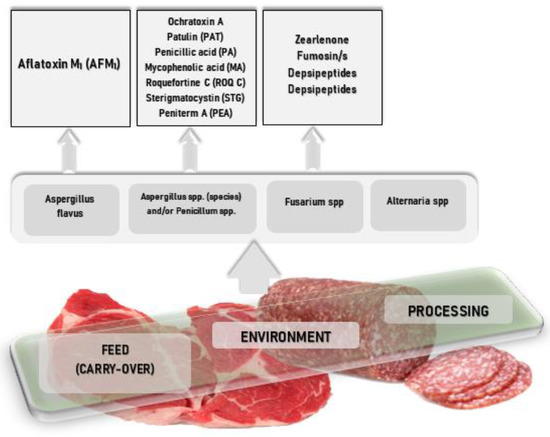
The control of the pathogenic load on foodstuffs is a key element in food safety. Particularly, seafood such as cold-smoked salmon is threatened by pathogens such as Salmonella sp. or Listeria monocytogenes. Despite strict existing hygiene procedures, the production industry constantly demands novel, reliable methods for microbial decontamination. Against that background, a microwave plasma-based decontamination technique via plasma-processed air (PPA) is presented. Thereby, the samples undergo two treatment steps, a pre-treatment step where PPA is produced when compressed air flows over a plasma torch, and a post-treatment step where the PPA acts on the samples. This publication embraces experiments that compare the total viable count (tvc) of bacteria found on PPA-treated raw (rs) and cold-smoked salmon (css) samples and their references. The tvc over the storage time is evaluated using a logistic growth model that reveals a PPA sensitivity for raw salmon (rs). A shelf-life prolongation of two days is determined. When cold-smoked salmon (css) is PPA-treated, the treatment reveals no further impact. When PPA-treated raw salmon (rs) is compared with PPA-untreated cold-smoked salmon (css), the PPA treatment appears as reliable as the cold-smoking process and retards the growth of cultivable bacteria in the same manner. The experiments are flanked by quality measurements such as color and texture measurements before and after the PPA treatment. Salmon samples, which undergo an overtreatment, solely show light changes such as a whitish surface flocculation. A relatively mild treatment as applied in the storage experiments has no further detected impact on the fish matrix.