Executive Summary of Findings
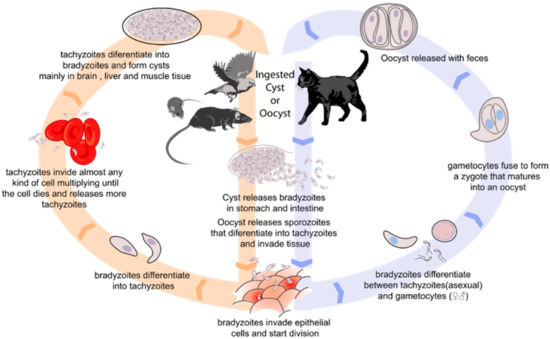
Cyclospora cayetanensis (C. cayetanensis) is a coccidian protozoan parasite, belonging
to the phylum Apicomplexa, order Eucoccidiorida, family Eimeriidae, described between 1993 to 1994 as a newly identified human gastrointestinal pathogen.
Within the genus Cyclospora, only C. cayetanensis is known to infect humans. However, recent advances in genomics separated C. cayetanensis into 3 proposed species, with the two new proposed species also considered parasitic to humans (Cyclospora ashfordi sp. nov. and Cyclospora henanensis sp. nov.).
For the purpose of this document and to reflect the proposed status of the new
nomenclature “C. cayetanensis” refers to all three species of Cyclospora parasitic in humans.
The parasite produces oocysts that are resistant to harsh environmental conditions and many
chemical treatments commonly used to reduce the presence of bacterial pathogens in the
specialty crop production environment and in agricultural inputs (e.g., agricultural water). C.
cayetanensis is the etiologic agent of cyclosporiasis, its host range is limited to humans.
Detected in association with human illness in many parts of the world, C. cayetanensis
previously was considered to be a pathogen acquired during childhood in developing nations.
In the United States, cyclosporiasis was previously associated with international travel or
consumption of contaminated imported foods. In recent years, the U.S. has seen an increase in cases and positive samples associated with domestically grown produce, both as raw
agricultural commodities and fresh cut. Laborers with the history of recent travel to countries
where C. cayetanensis is endemic have not been ruled out as the sources of the pathogen in
these outbreaks. Since 2016, the number of cyclosporiasis cases has increased approximately
3-fold, often linked to the consumption of leafy herbs and ready-to-eat salads. Fecal
contamination from symptomatic or asymptomatic carriers is, ultimately, the only known source of C. cayetanensis. The hypothesis that C. cayetanensis has become endemic in the production regions of the U.S. remains to be robustly supported. The hypothesis that farm workers with a history of recent travel to areas where the parasite is common are the likeliest source of the pathogen has not been ruled out. C. cayetanensis likely spreads via the fecal-environment-oral route when sanitation controls break down. Efforts have been made to develop molecular detection methods for C. cayetanensis in both food and environmental samples.
However, due to the high degree of genome-level conservation between C. cayetanensis and its close relatives that are not pathogenic in humans, results of some environmental surveys that relied solely on the PCR-based detection of ribosomal RNA genes likely overestimated the prevalence of C. cayetanensis. There remain significant knowledge and data gaps that hamper the implementation of effective measures to prevent the contamination of produce with the oocysts of this parasite. Awareness of the factors that can contribute to C. cayetanensis contamination of domestically grown and imported produce is key to developing an effective prevention and management strategy.