Gov UK
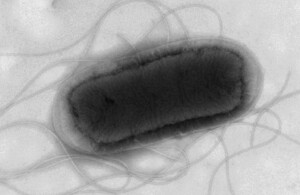
The UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA), together with public health agencies in Scotland, Northern Ireland and Wales, are investigating an increase in the number of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) cases in the UK in recent weeks.
Infections caused by STEC bacteria can cause severe bloody diarrhoea and, in some cases, more serious complications. It is often transmitted by eating contaminated food but can also be spread by close contact with an infected person, as well as direct contact with an infected animal or its environment.
Whole genome sequencing of samples in the current investigation indicates that most cases are part of a single outbreak. Based on the wide geographic spread of cases, it is most likely that this outbreak is linked to a nationally distributed food item or multiple food items. The source of this outbreak is not yet confirmed but there is currently no evidence linking the outbreak to open farms, drinking water or swimming in contaminated seawater, lakes or rivers. The public health agencies are working with the Food Standards Agency (FSA) and Food Standards Scotland to investigate further.
As of 4 June, there have been 113 confirmed cases associated with this outbreak of STEC O145 in the UK, all reported since 25 May 2024:
- 81 in England
- 18 in Wales
- 13 in Scotland
- 1 in Northern Ireland (for this case, evidence suggests that they acquired their infection while visiting England)
Typically, we see around 1,500 cases of STEC over a full year. Numbers of confirmed cases associated with this outbreak are expected to rise as further samples undergo whole genome sequencing.
Cases range in age from 2 years old to 79 years old, with the majority of cases in young adults. Of the 81 cases identified to date in England, 61 have provided information to UKHSA related to food, travel and potential exposures and of these we know that 61% have been hospitalised.
While the source of this outbreak is currently unknown, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of gastrointestinal infections, as well as limiting the spread to others:
- regularly wash your hands with warm water and soap — alcohol gels do not kill all bugs that cause diarrhoeal illness
- follow food hygiene measures such as washing fruit and vegetables and cooking food properly
- if you have diarrhoea and vomiting, you should not prepare food for others and avoid visiting people in hospitals or care homes to avoid passing on the infection
- you should not return to work, school or nursery until 48 hours after your symptoms have stopped
Trish Mannes, Incident Director at UKHSA, said:
Symptoms of infections with STEC include severe and sometimes bloody diarrhoea, stomach cramps, vomiting and fever. If you have diarrhoea and vomiting, you can take steps to avoid passing it on to family and friends. NHS.UK has information on what to do if you have symptoms and when to seek medical advice.
Washing your hands with soap and warm water and using disinfectants to clean surfaces will help stop infections from spreading. If you are unwell with diarrhoea and vomiting, you should not prepare food for others and avoid visiting people in hospitals or care homes to avoid passing on the infection in these settings. Do not return to work, school or nursery until 48 hours after your symptoms have stopped.
Darren Whitby, Head of Incidents and Resilience at the FSA, said:
The FSA is working with UKHSA and relevant Public Health bodies to identify the source of the illness, which is likely to be linked to one or more food items.
We always advise consumers and those looking after vulnerable people to ensure good hygiene practices are followed when handling and preparing food, regularly washing hands with soap and warm water and ensuring equipment, utensils and surfaces foods come into contact with are cleaned thoroughly to prevent cross contamination.
You should not prepare food for others if you have had symptoms, or for 48 hours after symptoms stop. You can find more information about good hygiene practises – 4c’s, and E. coli on our website.
Jim McMenamin, Head of Health Protection (infection Services), Public Health Scotland, said:
To help stop infections like E. coli from spreading, we advise regular hand washing using soap and water, particularly after using the toilet and before preparing food. People should also use disinfectants to clean surfaces that may be contaminated. Anyone experiencing severe and sometimes bloody diarrhoea, stomach cramps, vomiting and fever should call their GP or 111 to seek advice. Anyone with diarrhoea or vomiting should avoid attending places such as schools, workplaces or social gatherings until at least 48 hours after their symptoms have ceased.
Wendi Shepherd, Consultant in Health Protection for Public Health Wales, said:
Public Health Wales is working with partners in the UK and across the Welsh NHS to investigate this incident. There are currently 18 cases identified in Wales and healthcare providers have been advised of the increase in cases. We would advise anyone who has experienced bloody diarrhoea or severe stomach cramps to seek medical attention.