Archives
-
Join 343 other subscribers
KSWFoodWorld
Blog Stats
- 431,446 Views
Category Archives: Lactobacillus plantarum
Research – Inactivation of Foodborne Pathogens by Lactobacillus Strains during Meat Fermentation: Kinetics and Mathematical Modelling
This study examined the effect of beef fermentation with Lactiplantibacillus paraplantarum (L) PTCC 1965, Lactiplantibacillus (L) plantarum subsp. plantarum PTCC 1745, and Lactiplantibacillus (L) pentosus PTCC 1872 bacteria on the growth of pathogenic bacteria, including Salmonella (S) Typhi PTCC 1609 and Staphylococcus (S) aureus PTCC 1826. The growth of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) and the effect of fermentation on pathogenic bacteria were studied using Weibull: biphasic linear and competitive models. The results showed that the rate of pH reduction was lower in the early stages and increased as the microbial population grew. The α parameter was lower for L. plantarum subsp. plantarum compared to L. paraplantarum and L. pentosus. The comparison of the α parameter for bacterial growth and pH data showed that the time interval required to initiate the rapid growth phase of the bacteria was much shorter than that for the rapid pH reduction phase. The pH value had a 50% greater effect on the inactivation of S. Typhi when compared to the samples containing L. plantarum subsp. plantarum and L. pentosus. The same parameter was reported to be 72% for the inactivation of St. aureus. In general, during the fermentation process, LAB strains caused a decrease in pH, and as a result, reduced the growth of pathogens, which improves consumer health and increases the food safety of fermented meat.
Posted in Decontamination Microbial, Food Micro Blog, Food Microbiology, Food Microbiology Blog, Food Microbiology Research, Food Microbiology Testing, lactic acid bacteria, Lactobacillus, Lactobacillus plantarum, microbial contamination, Microbial growth, Microbiological Risk Assessment, Microbiology, Microbiology Investigations, Microbiology Risk
Research – Special Issue: Beneficial Properties and Safety of Lactic Acid Bacteria
The application of LAB in various sectors, including in the biotechnical and food industry, in human and veterinary practice, and in health-promoting practices and cosmetics, has been the subject of intensive research across the globe, with a range of traditional and innovative methods currently being explored. The rediscovery of old practices, the establishment of new processes based on the production and application of different metabolites produced by LAB, and the formation of novel perspectives on the fermentation processes initiated by LAB, have become areas of significant interest in recent years. Various antimicrobial peptides, including bacteriocins, have been proposed as alternatives to antibiotics or have been suggested for use as their synergistic “partners”. The application field of probiotics is being widened to encompass new innovative areas that are targeted towards personalized practice, with the aim of improving human health. An increasingly extensive understanding of bioactive peptides has heralded their application in practices that are alternative or complementary to Western medicine. Approaches to bio-preservation require fewer chemical preservatives and are, currently, thoroughly explored in food research. The enrichment and fortification of food products with biologically active metabolites, including vitamins, antimicrobials, and immunomodulators, are only some of the research areas that ought to be explored as options for the application of various LAB in the food industry.
The concepts associated with the beneficial properties and safety of LAB have been, and always need to be, jointly explored. Even if several LAB strains have been applied historically as safe and beneficial cultures, various other representatives of LAB have been documented as human and animal pathogens, as phytopathogens, and as also including strains associated with spoilage and deterioration [1]. LAB represent a universe of varied microorganisms, with all of them characterized as Gram-positive, catalase negative, as possessing a common metabolism and as initiating the formation of a similar end product (lactic acid) as a result of carbohydrate fermentation [2]. As a diverse group of microorganisms, they are adapted to various ecosystems and environmental conditions, and can grow at different temperatures and use a variety of carbon sources [1,2]. They are associated with virtually all living forms, from simple eukaryotic organisms and plant material, to the skin and GIT of vertebrates, insects, mollusks, crustaceans, etc. They may be described as either beneficial or as pathogens, but they always possess a clear ecological role in numerous life cycles [2]. Of particular note are species such as Enterococcus spp., some of which are unmistakably opportunistic pathogens and, when associated with vancomycin resistance, pose a serious health threat to humans and to animals [3]; these pathogens are typically associated with nosocomial infections [3]. Simultaneously, however, LAB also comprise species that play a beneficial role in the production of various plants, dairy and meat fermented food products [4], or even as probiotics [5]. It has been suggested that enterococci are producers of bacteriocins, some of which can be applied in the control of food-borne and hospital-associated (human and veterinary) pathogens [6]. However, before proposing a strain, even one belonging to a species with a history of safe application, its safety properties must be appropriately evaluated; this is a necessary and essential step that must be completed prior to its application in food fermentation, as a probiotic for human and animals, in human and veterinary medicine, or in agricultural practices. The novel tools utilized in the evaluation of the safety of microbial cultures, including DNA-associated experimental approaches, have become routine in the last two decades. Considering this, the validation of safety, both of new microbial and currently applied cultures, is now considered essential. In addition to “classical” PCR-based approaches, whole genome sequencing and the appropriate analysis of the generated data have become routine in the evaluation of the safety profile of microbial cultures [7,8,9].
Posted in Food Microbiology Blog, Food Microbiology Research, Food Microbiology Testing, LAB, lactic acid bacteria, Lactobacillus, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus sakei, Lactobacillus saki, Lactococcus, microbial contamination, Microbial growth, Microbiological Risk Assessment, Microbiology, Microbiology Investigations, Microbiology Risk
Research – Bread Biopreservation through the Addition of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Sourdough
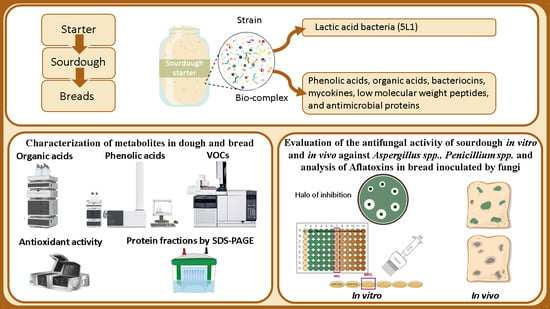
Abstract
Nowadays, the consumer seeks to replace synthetic preservatives with biopreservation methods, such as sourdough in bread. Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) are used as starter cultures in many food products. In this work, commercial yeast bread and sourdough breads were prepared as controls, as well as sourdough breads with L. plantarum 5L1 lyophilized. The impact of L. plantarum 5L1 on the properties of bread was studied. Antifungal compounds and the impact on the protein fraction by the different treatments in doughs and breads were also analyzed. In addition, the biopreservation capacity of the treatments in breads contaminated with fungi was studied and the mycotoxin content was analyzed. The results showed significant differences with respect to the controls in the properties of the bread and a higher total phenolic and lactic acid content in breads with higher amounts of L. plantarum 5L1. In addition, there was a higher content of alcohol and esters. Furthermore, adding this starter culture produced hydrolysis of the 50 kDa band proteins. Finally, the higher concentration of L. plantarum 5L1 delayed fungal growth and reduced the content of AFB1 and AFB2 compared to the control.
Posted in antifungal, Decontamination Microbial, Food Micro Blog, Food Microbiology, Food Microbiology Blog, Food Microbiology Research, Food Microbiology Testing, fungi, LAB, lactic acid bacteria, Lactobacillus, Lactobacillus plantarum, microbial contamination, Microbial growth, Microbiological Risk Assessment, Microbiology, Microbiology Investigations, Microbiology Risk
Research – Bioprotective Lactic Acid Bacteria and Lactic Acid as a Sustainable Strategy to Combat Escherichia coli O157:H7 in Meat
Abstract
Human infection by Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) constitutes a serious threat to public health and a major concern for the meat industry. Presently, consumers require safer/healthier foods with minimal chemical additives, highlighting the need for sustainable solutions to limit and prevent risks. This work evaluated the ability of two antagonistic lactic acid bacteria (LAB) strains, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum CRL681 and Enterococcus mundtii CRL35, and their combination in order to inhibit EHEC in beef (ground and vacuum sealed meat discs) at 8 °C during 72 h. The effect of lower lactic acid (LA) concentrations was evaluated. Meat color was studied along with how LAB strains interfere with the adhesion of Escherichia coli to meat. The results indicated a bacteriostatic effect on EHEC cells when mixed LAB strains were inoculated. However, a bactericidal action due to a synergism between 0.6% LA and LAB occurred, producing undetectable pathogenic cells at 72 h. Color parameters (a*, b* and L*) did not vary in bioprotected meat discs, but they were significantly modified in ground meat after 24 h. In addition, LAB strains hindered EHEC adhesion to meat. The use of both LAB strains plus 0.6% LA, represents a novel, effective and ecofriendly strategy to inactivate EHEC in meat.
Posted in EHEC, Food Micro Blog, Food Microbiology, Food Microbiology Blog, Food Microbiology Research, Food Microbiology Testing, LAB, Lactobacillus, Lactobacillus plantarum, microbial contamination, Microbial growth, Microbiological Risk Assessment, Microbiology, Microbiology Investigations, Microbiology Risk, STEC, STEC E.coli
Research – Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of lactic acid to reduce microbiological surface contamination on carcases from kangaroos, wild pigs, goats and sheep
Studies evaluating the safety and efficacy of lactic acid to reduce microbiological surface contamination from carcases of wild game (i.e. kangaroos and wild pigs) and small stock (i.e. goats and sheep) before chilling at the slaughterhouse were assessed. Wild pig and kangaroo hide‐on carcases may have been chilled before they arrive at the slaughterhouse and are treated after removal of the hides. Lactic acid solutions (2–5%) are applied to the carcases at temperatures of up to 55°C by spraying or misting. The treatment lasts 6–7 s per carcass side. The Panel concluded that: [1] the treatment is of no safety concern, provided that the lactic acid complies with the European Union specifications for food additives; [2] based on the available evidence, it was not possible to conclude on the efficacy of spraying or misting lactic acid on kangaroo, wild pig, goats and sheep carcases; [3] treatment of the above‐mentioned carcases with lactic acid may induce reduced susceptibility to the same substance, but this can be minimised; there is currently no evidence that prior exposure of food‐borne pathogens to lactic acid leads to the occurrence of resistance levels that compromise antimicrobial therapy; and [4] the release of lactic acid is not of concern for the environment, assuming that wastewaters released by the slaughterhouses are treated on‐site, if necessary, to counter the potentially low pH caused by lactic acid, in compliance with local rules.
Posted in cross contamination, Decontamination Microbial, food contamination, Food Micro Blog, Food Microbiology, Food Microbiology Blog, Food Microbiology Research, Food Microbiology Testing, LAB, lactic acid bacteria, Lactobacillus, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus sakei, Lactobacillus saki, Lactococcus, microbial contamination, Microbiological Risk Assessment, Microbiology, Microbiology Investigations, Research
Research – Role of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Food Preservation and Safety
Fermentation of various food stuffs by lactic acid bacteria is one of the oldest forms of food biopreservation. Bacterial antagonism has been recognized for over a century, but in recent years, this phenomenon has received more scientific attention, particularly in the use of various strains of lactic acid bacteria (LAB). Certain strains of LAB demonstrated antimicrobial activity against foodborne pathogens, including bacteria, yeast and filamentous fungi. Furthermore, in recent years, many authors proved that lactic acid bacteria have the ability to neutralize mycotoxin produced by the last group. Antimicrobial activity of lactic acid bacteria is mainly based on the production of metabolites such as lactic acid, organic acids, hydroperoxide and bacteriocins. In addition, some research suggests other mechanisms of antimicrobial activity of LAB against pathogens as well as their toxic metabolites. These properties are very important because of the future possibility to exchange chemical and physical methods of preservation with a biological method based on the lactic acid bacteria and their metabolites. Biopreservation is defined as the extension of shelf life and the increase in food safety by use of controlled microorganisms or their metabolites. This biological method may determine the alternative for the usage of chemical preservatives. In this study, the possibilities of the use of lactic acid bacteria against foodborne pathogens is provided. Our aim is to yield knowledge about lactic acid fermentation and the activity of lactic acid bacteria against pathogenic microorganisms. In addition, we would like to introduce actual information about health aspects associated with the consumption of fermented products, including probiotics.
Posted in Food Micro Blog, Food Microbiology, Food Microbiology Blog, Food Microbiology Research, Food Microbiology Testing, LAB, lactic acid bacteria, Lactobacillus, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus sakei, Lactobacillus saki, microbial contamination, Microbiological Risk Assessment, Microbiology, Microbiology Investigations, Research
Research – Lactic Acid Bacteria as Antimicrobial Agents: Food Safety and Microbial Food Spoilage Prevention
In the wake of continual foodborne disease outbreaks in recent years, it is critical to focus on strategies that protect public health and reduce the incidence of foodborne pathogens and spoilage microorganisms. Currently, there are limitations associated with conventional microbial control methods, such as the use of chemical preservatives and heat treatments. For example, such conventional treatments adversely impact the sensorial properties of food, resulting in undesirable organoleptic characteristics. Moreover, the growing consumer advocacy for safe and healthy food products, and the resultant paradigm shift toward clean labels, have caused an increased interest in natural and effective antimicrobial alternatives. For instance, natural antimicrobial elements synthesized by lactic acid bacteria (LAB) are generally inhibitory to pathogens and significantly impede the action of food spoilage organisms. Bacteriocins and other LAB metabolites have been commercially exploited for their antimicrobial properties and used in many applications in the dairy industry to prevent the growth of undesirable microorganisms. In this review, we summarized the natural antimicrobial compounds produced by LAB, with a specific focus on the mechanisms of action and applications for microbial food spoilage prevention and disease control. In addition, we provide support in the review for our recommendation for the application of LAB as a potential alternative antimicrobial strategy for addressing the challenges posed by antibiotic resistance among pathogens. View Full-Text
Posted in antimicrobial resistance, Antimicrobials, Decontamination Microbial, Food Micro Blog, Food Microbiology, Food Microbiology Blog, Food Microbiology Research, Food Microbiology Testing, Food Technology, LAB, lactic acid bacteria, Lactobacillus, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus sakei, Lactobacillus saki, Lactococcus, microbial contamination, Microbiological Risk Assessment, Microbiology, Research
Research – Anti‐adhesive effects of sialic acid and Lactobacillus plantarum on Staphylococcus aureus in vitro
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is a common food‐borne pathogen that causes severe diseases after adhesion to epithelial cells. Lactobacillus inhibits pathogenic bacterial adhesion and infection. In addition, sialic acid (SA) is widely known for its beneficial biological functions. A new way of reducing the occurrence of diseases and curbing the overuse of antibiotics is ingesting prebiotics and probiotics that regulate the intestinal flora. In this study, we first evaluated the anti‐adhesive effects of several strains of Lactobacillus on S. aureus. The study revealed that the S. aureus adhesion was inhibited by all the strains of Lactobacillus. Besides, the rate of inhibition by L. plantarum Z‐4 was significantly higher than other Lactobacillus species. We then investigated the effects of different SA concentrations (40, 100, 150, 200, and 260 μg/ml) on the growth and adhesion characteristics of L. plantarum and S. aureus. The results showed that SA influences bacterial adhesion by regulating the bacteria’s growth characteristics. Finally, the effects of SA combined with Lactobacillus on the adhesion of S. aureus were assessed by competition, exclusion and displacement methods. SA with a concentration of 260 μg/mL combined with L. plantarum had the highest inhibition effect on the competition assays. In addition, the expression of S. aureus adhesion‐related genes was reduced. This provides a new perspective on the application of SA and/or L. plantarum and its potential to resist adhesion of S. aureus.
Posted in food contamination, Food Micro Blog, Food Microbiology, Food Microbiology Blog, Food Microbiology Research, Food Microbiology Testing, Food Pathogen, Food Poisoning, food recall, Food Safety, Food Technology, Food Testing, Lactobacillus plantarum, Research, Staphylococcus aureus, Technology
RASFF Alert- Animal Feed – unauthorised ingredients in fish feed

unauthorised ingredients (Lactobacillus plantarum, Enterococcus faecalis, Pediococcus lactis) in fish feed from China in the UK
Research – Modeling the interactions among Salmonella enteritidis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa , and Lactobacillus plantarum
This paper was to investigate the interactions among Salmonella enteritidis, Lactobacillus plantarum , and Pseudomonas aeruginosa at four combinations of initial concentration. Firstly, fitting the growth curves to obtain growth parameters—lag time (λ ), maximal growth rate ( μ max), initial concentration (N 0), and maximum population density (N max) for each strain in monocultures or cocultures. Then interactions among S. enteritidis, P. aeruginosa , and L. plantarum in cocultures at four combinations of initial concentration were quantified by the Lotka–Volterra model with six interaction coefficients. Results indicated that there were no interactions between S. enteritidis and P. aeruginosa ; S. enteritidis and P. aeruginosa had an inhibitory effect on L. plantarum , but L. plantarum had no effects on another two. Besides, the higher the initial concentrations of S. enteritidis or P. aeruginosa , the lower the growth potential of L. plantarum . This study provided more accurate predictions for the growth of bacteria under actual food contamination conditions.

