Feature Article
Shellfish Poisoning
The Centre for Food Safety (CFS) received in April 2023 a referral from the Centre for Health Protection of a suspected case of diarrhoetic shellfish poisoning in which the affected persons developed diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain within an hour after consuming venus clams at a restaurant. This article gives a brief introduction on shellfish poisoning.
What is Shellfish Poisoning?
Shellfish poisoning is caused by shellfish toxins produced by certain species of algae. When shellfish eat toxin-producing algae, the toxins can accumulate in their tissue. Consumption of shellfish containing shellfish toxins by humans can cause a variety of gastrointestinal and neurological illnesses, known as shellfish poisoning. Examples of shellfish that have been involved in shellfish poisoning include mussels, clams, oysters, scallops and geoducks.
Numerous shellfish toxins have been discovered around the world; they could cause different types of shellfish poisoning. Five major types of shellfish poisoning are discussed below:
(i) Paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) — caused by paralytic shellfish toxins (PSTs), which are a group of water-soluble alkaloid neurotoxins, including saxitoxins (STXs).
(ii) Diarrhoetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) — caused by diarrhoetic shellfish toxins (DSTs), which are a group of lipid-soluble polyether toxins, including okadaic acid (OA).
(iii) Neurotoxic shellfish poisoning (NSP) — caused by neurotoxic shellfish toxins (NSTs), which are a group of lipid-soluble polyether toxins, including brevetoxins (BTXs).
(iv) Amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP) — caused by amnesic shellfish toxins (ASTs), including the water-soluble amino acid domoic acid (DA).
(v) Azaspiracid shellfish poisoning (AZP) — caused by azaspiracid shellfish toxins (AZTs), including the lipid-soluble toxin azaspiracid (AZA).
Characteristics of Shellfish Toxins
Different groups of shellfish toxins display multifarious chemical structures, which can be broadly classified into amino acids (DA), alkaloids (STXs) and polyketides (OA, BTXs and AZA).
The reasons why some algae produce shellfish toxins remain unknown. These toxins are secondary metabolites with no explicit function for the algae. They are probably used by the algae to compete for space, defence against predators or prevent the overgrowth of other organisms.
In general, shellfish toxins are heat stable, odourless, tasteless and not destroyed by cooking, freezing or other food preparation procedures. It is hard to distinguish between toxic and non-toxic shellfish visually.
Bioaccumulation of Shellfish Toxins in Bivalve Molluscs
Algae are part of the natural diet of bivalve molluscs. After shellfish has ingested shellfish toxin-producing algae, shellfish toxins will accumulate and concentrate in their internal organs, such as hepatopancreas of bivalves (Figure 1). Generally speaking, the adductor muscle contains only a low level of shellfish toxins.
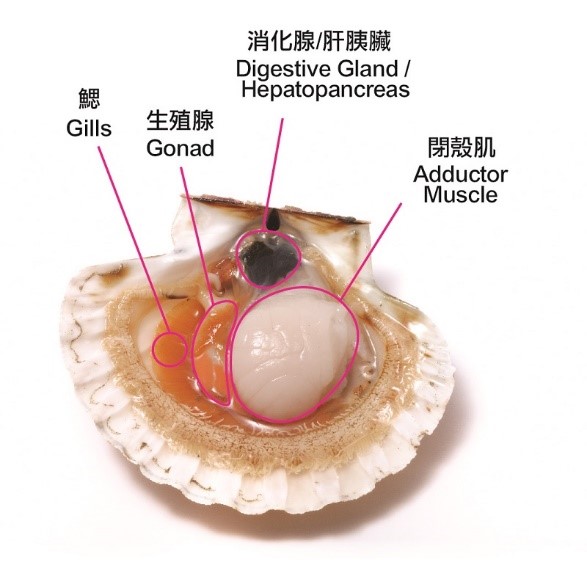
Figure 1: Internal parts of a scallop
Symptoms of Shellfish Poisoning
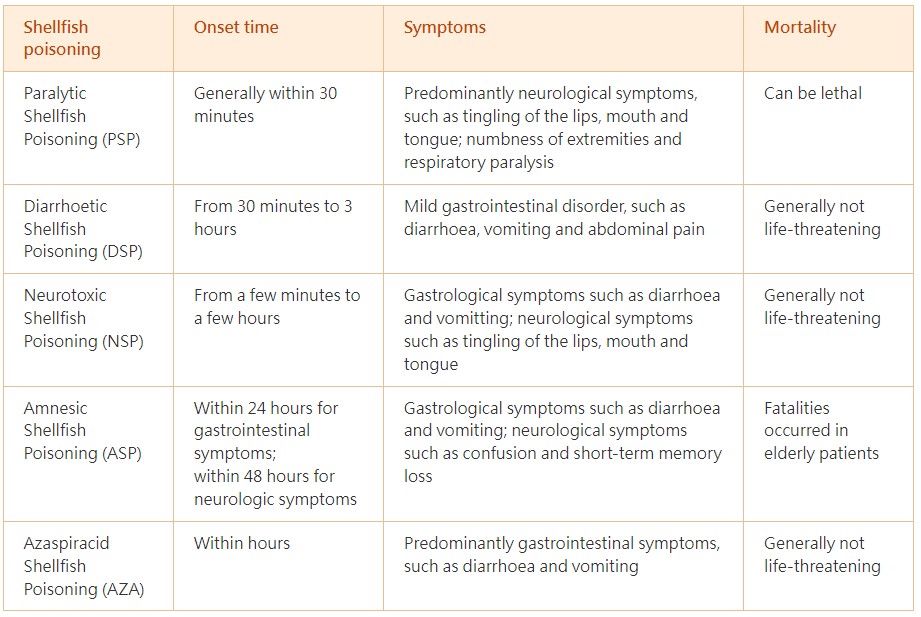
Shellfish toxins can cause a wide variety of symptoms in humans, depending on the type and amount of toxins ingested. Symptoms of different types of shellfish poisoning are summarised below:
Safety Levels of Shellfish Toxins
The toxicity of various shellfish toxins was evaluated by a joint expert working group of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO in 2004. Acute reference doses (ARfDs) (i.e. the amount of toxins that can be ingested in a period of 24 hours or less without appreciable health risk) have been established for these shellfish toxins. In addition, the Codex Alimentarius Commission (Codex) has established the maximum levels (MLs) for shellfish toxins in edible parts (the whole or any part intended to be eaten separately) of live bivalve molluscs. While the ARfDs are critical in assessing the safety of food in terms of the level of shellfish toxins contained, Codex MLs are the levels recommended by Codex to be permitted in shellfish.
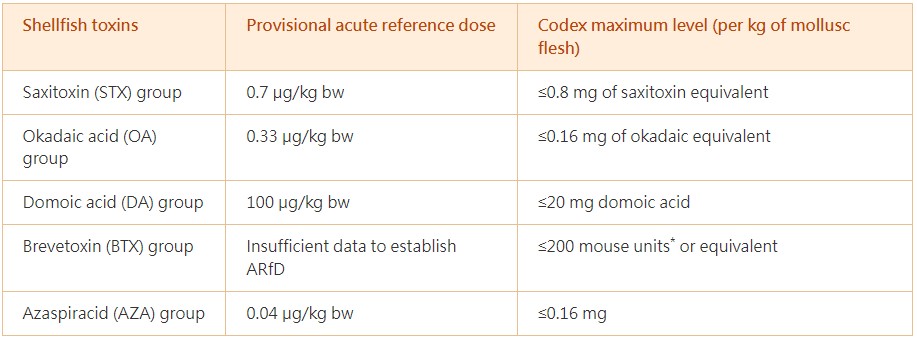
*An estimate of toxicity of the toxin made by mouse bioassay.
Key Points to Note
- Shellfish toxins are heat stable, odourless, tasteless and not destroyed by cooking, freezing or other food preparation procedures.
- It is hard to distinguish between toxic and non-toxic shellfish visually.
- In general, shellfish toxins accumulate and concentrate in the internal organs of bivalves.
Advice to Consumers
- Purchase shellfish from reliable sources.
- To reduce the health risk of shellfish poisoning, remove and discard all internal organs of shellfish where possible before consumption.
- Seek medical attention immediately if you feel ill after eating shellfish.


