This year’s report summarizes 2022 preliminary surveillance data. It describes 2022 incidence compared with the average incidence for 2016–2018, the reference period used for the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Healthy People 2030 goals. The report also summarizes cases of hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) during 2021.
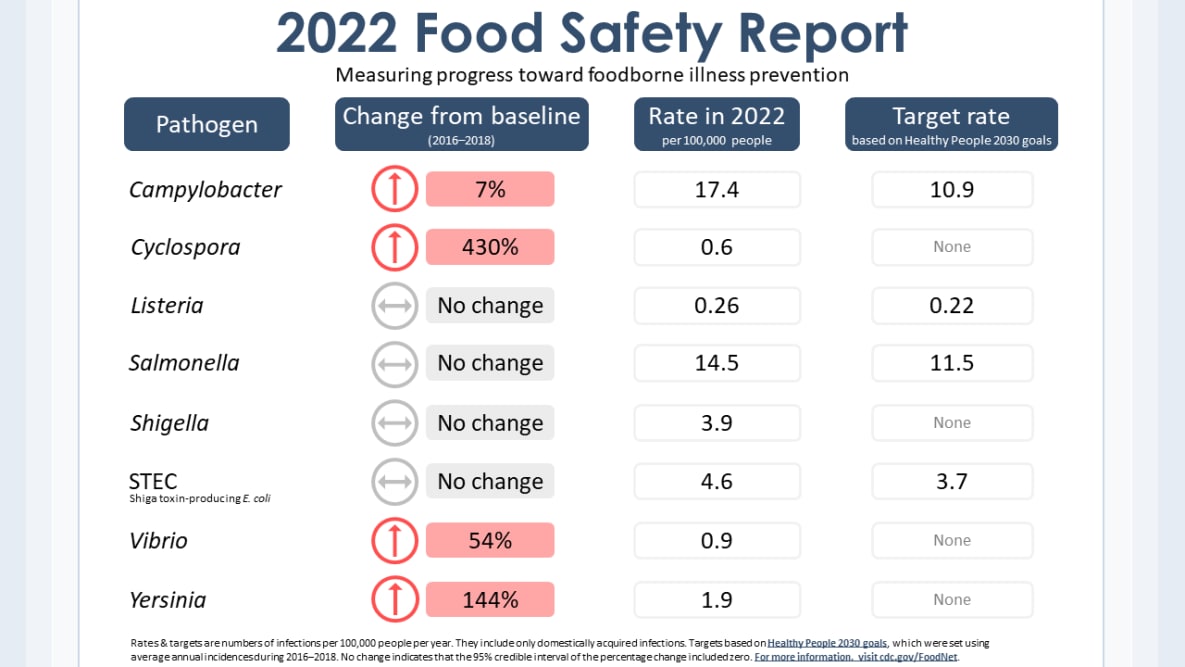
- In 2022, enteric (intestinal) infections monitored by FoodNet generally returned to or exceeded levels observed in 2016–2018 (before the COVID-19 pandemic).
- Incidence of Campylobacter, Listeria, Salmonella, and Shigella infections did not change in 2022 compared with 2016–2018.
- Incidence of Cyclospora, STEC, Vibrio, and Yersinia infections increased in 2022 compared with 2016–2018.
- Campylobacter and Salmonella remain the top causes of enteric infections monitored by FoodNet.
- Increased use of CIDTs contributed to the increased detection of infections.
- FoodNet data show lack of progress during 2022 toward Healthy People 2030 goals for reducing foodborne illness. Concerted efforts are needed to implement effective prevention strategies to reduce disease burden.

